Functionality of the Parallel Application Window
Initialization:
There are several initialization for the Java GUI interface before it interacts
with users:
- Connect to data base through JDBC -- Currently the PostgreSQL data
base is installed on the host blueser.cpdc.ece.nwu.edu.
Suppose user
id is wkliao, a data base named wkliao has been created
and the Java GUI should be able to query from this data base.
- Find all parallel applications -- A table named
application_table has
already existed in database wkliao.
It stores information for all applications registered in the database
including application name, host name (to be run on), path + file name
of the execution file, application version, run-time parameter names, and
time of registration.
- The Name menu -- When users click the Name menu,
it should pull down a list of registered application names and users can
pick one to run. When users choose a listed application, Java GUI should
get the run-time parameters for this application from the data base and
display in the following window of Run-Time Parameters.
In the example of astro3d, they are nproc, dimZ, dimY, and
dimZ. These parameters are required by users' input and will
be appended to the command line arguments when running the application.
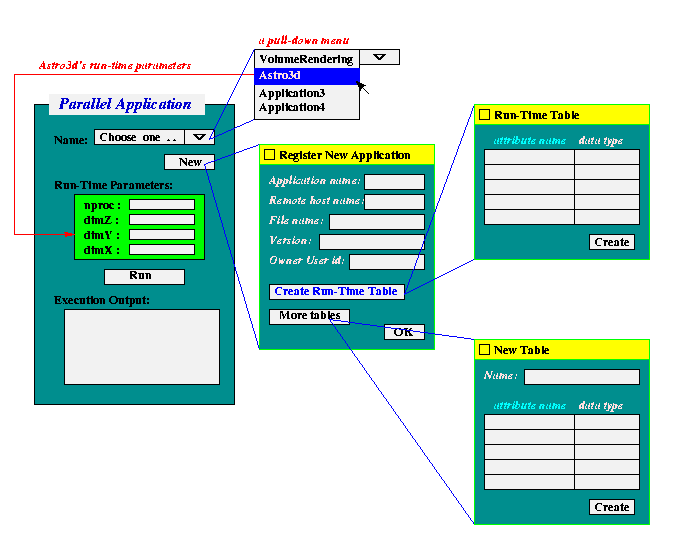
Figure 1. Parallel Application Window
Running a Registered Application:
Once users choose an application, fill out the run-time parameter values, and
click the Run button, the GUI should be able to execute the file on the
remote system. For example, a command using remote shell to run
astro3d at aixdev on 4 processors can be:
% rsh -l wkliao aixdev codes/Run/astro3d 4 16 16 16
and its output.
Another example runs the data analysis program on all data sets of astro3d
application using 4 processors:
% rsh -l wkliao aixdev codes/Run/data_analysis 4 astro3d
Or it can be implemented by using other methods to run applications remotely.
- Check run-time parameters -- Java GUI should be able to check if
the type of users' input values are valid. Take astro3d as an example,
the input for three dimension should be all integers. This information
should be able to obtain from the data base.
- Display the output in the output window -- The application's
running output should be re-direct to the Output window.
Here is an example of running output of
program astro3d.
Register a New Application:
Users can register a new application by clicking the New button.
At least following actions should be carried out:
- Register new application -- Click New button will pop up a window
for users to register a new applications. This window should contains
information of running the application: such as application name (to be
referred in the future), remote host name, remote user id, path (relative
to user's home directory) and file name, version, etc. Java GUI should
write these information into
application_table in the
database.
- Run-Time Table -- At least the Run-Time table,
run_table, of this new
application should be created by the users. Other tables, including
dataset_table,
access_pattern_table,
execution_table,
storage_pattern_table,
can be created internally by Java GUI.
When clicking Create Run-Time Table button, a new pop-up window
is shown for users' input on the table's field's names and its initial
values (optional).
- Other tables -- Given table names, users can create other tables
in a similar manner. All tables will be created in the data base with the
application name as the prefix.
Last modified on Oct. 19, 1999
Please send comments to
wkliao@ece.nwu.edu.

