Multicast Call Admission Control in Wide Area ATM Network
--Saurav Chopra, Deptt of Electrical
Engg ,IIT Delhi ,New Delhi-110016.
Call Admission is important in ATM networks to provide the Quality of
Service objective and proper network utilization. Existing work on call
admission has focused on point to point connection requests. Multicasting,
which involves many - to- many communication is becoming important with
growing interest in video conferencing and distance education. Admitting
a multicast call into the network without considering the repercussions
may hamper the quality of service for existing calls. In this paper we
study the problem of multicast call admission and propose an overall solution
for the problem introducing a new routing scheme based on a single virtual
connection which greatly simplifies the call admission control.
1. Background:
1.1 ATM Networks:
With the rapid growth of the World Wide Web and telecommunication applications
like distance education , audio and video conferencing a need has been
experienced to provide B-ISDN ( Broadband - Integrated Services Digital
Network), that is an integrated network which provides capacity to carry
all kinds of information namely audio, video and data , thus leading to
sources of vastly different bit rates and different statistical nature.
Multimedia applications typically place a huge demand on the networks resources
and also sometimes require performance guarantees on the quality of service
to be maintained. Keeping the above mentioned requirements in mind ATM
(Asynchronous Transfer Mode) has been recognised as a very effective network
technology and has been made possible through recent advances in fibre
optics, VLSIís and microprocessors.
1.2 Multicasting :
Multicast communication is defined as one in which messages are concurrently
sent to multiple destinations from single or multiple sources. Some of
the typical uses of multicasting are mentioned below:
- distributed file systems requiring replication
- any form of conferencing (audio, video or data)
- distribution of audio &commercial television by digital networks
There are many ways in which multicast can be implemented:-
- Flooding : every incoming packet is sent on every outgoing line
except the one it arrived on, thus creating a large no of duplicate packets
- Multiple Unicast : that is treating a multicast connection between
multiple members as multiple connections between single users
- Setting up of Multicast tree using Routing Algorithms
This method has been most discussed in literature because of its ability
to satisfy QOS guarantees and provide optimum network utilisation
- A single virtual connection (VC) based multicasting which has
not been explored earlier but we seek to study in detail.
1.3 Call Admission Control(CAC):
CAC is defined as a set of actions taken at the time of connection set
up to judge whether the connection can be accepted. Thus we see that CAC
is essentially a preventive control mechanism to prevent network congestion,
help maintaining the QOS and at the same time ensure proper network utilisation.
The advantage which a preventive control mechanism holds over network congestion
algorithms like Usage Parameter Control , Resource Management or other
feedback control algorithms is that it is much faster which is very important
as ATM is typically a very high speed network.
2. Multicast Call Admission Control(CAC)
2.1 Difficulties in Multicast CAC:
- Checking for QOS: Checking for delay bounded transmission
becomes even more complicated , for example if we use the concept of multicast
trees.
- Incorporation of Virtual Paths in multicasting puts a heavy
load on the network hardware as for multicast traffic ,which is just 5-10%
of the traffic usually, we have to use multicast switches everywhere.
- Shared multicast, that is multicasting involving multiple sources
is very difficult to implement using multicast trees because one might
have to construct different multicast trees for each source .
- Dynamic Multicast , that is , multicasting in which multicast
group members can join and leave multicast session midway is also very
difficult to implement , as it might lead to change in whole multicast
tree structure .
2.2 A single virtual connection based multicast routing as solution
:
In order to simplify the connection admission control procedure we suggest
a simple single virtual connection based routing .
Implementation:
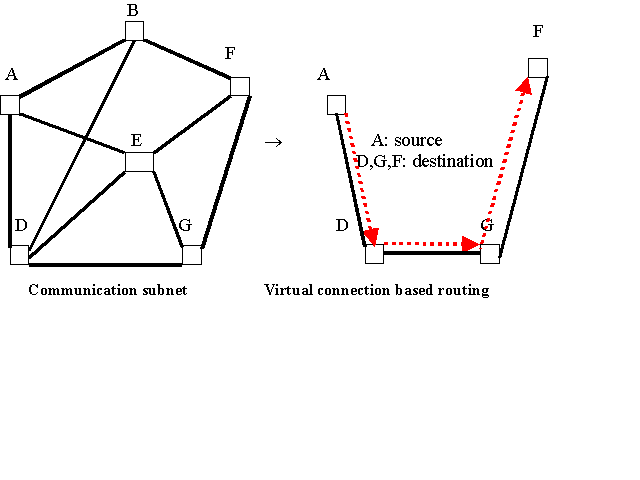
- Network Model & architecture: ADGF :single virtual connection.
AD,DG, GF : virtual paths. A, D,G,F are necessarily VC (virtual connection)
switches which need only generate two copies, instead of multiple copies
in a multicast tree.
- Routing Algorithm: The routing algorithm essentially used like
in the previous case of multicast trees can be constrained , unconstrained
to generate minimum cost paths. The routing algorithm is a suitable extension
of unicast routing algorithms by taking two nodes at a time ( with certain
bounds) and applying the unicast algorithms to these two nodes and so on
extending the multicast group. he routing which we have considered generates
minimum cost path at the same time satisfying the delay bound set by the
QOS. In our case it essentially reduces to a problem of ordering the nodes
on the basis of certain criterion (in our case spatial distribution of
nodes). Once the node have been ordered we generate a path by connecting
two nodes at a time using individual delay bounds for two elements at a
time, for e.g. our ordering is D , G, F . Now we will provide a D
1 delay bound for AD ,D 2 delay bound for DG
and D 3 for GF .These delay bounds are somehow
dependent on the overall delay bound(D ) and
the relative spatial locations. Two points can then be connected using
the DBOC (Delay bounded optimum cost ) algorithm to generate optimum cost
tree.
Heuristic for Path Based Multicasting:
- Order the nodes in the multicast group. This is the most important
aspect of the heuristic .
- Initially start with the first node and put it in multicast path and
arbitrarily assign L , length of multicast path to be 1 . P= M[1] , L=1.
(P: multicast path, M: multicast group. )
- Repeat the following step until all nodes in M are covered.
- S= P[L], the last node in the path till now.
- Pí= a delay bounded path from ĎSí to ĎDí ,which can be found using
a modification Djikstra's algorithm, where D ( a destination node in M
which is not a part of P)
- P=P @ Pí
3.0 Result:
Sample comparison of the connection and tree for same communication
subnet
 (
(
(The weights shown on the links show the cost and time delay parameters
associated with each link respectively)
F: source , B,D,E,H destination nodes :
Minimum Steiner Tree Cost:21 delaymax(end to end):5
Single multicast connection FDEHGB ,cost: 23 : delaymax(end to end): 7
Thus the single multicast connection performance is a little inferior to
the multicast tree based algorithm, but at the same time it provides a
lot of advantages with respect to tree based algorithms which are discussed
below.
4.0 Conclusion :
Thus in this paper we discuss a new routing scheme based on a single
virtual connection that greatly simplifies Multicast CAC as opposed to
tree based Multicast CAC .Certain advantages that
this new CAC method provides are :-
- CAC becomes very simple . Essentially the CAC is reduced to
finding a single path joining all the destination and source nodes, which
satisfies the bandwith requirements of the call and also the Quality of
Service paramters.
- Incorporation of Virtual Paths :which is very useful for proper
network utilisation, is easy because we only need VC switches which can
generate two copies and hence impose no unnecessary load on the network
hardware.
- Dynamic and Shared Multicast is also taken care of because
of the existence of a single connection joining all nodes . When a new
node wants to join or leave the multicast group only a part of the whole
connection needs to be modified and a whole new connection need not be
setup, as the same connection can be used for all the sources.
- Simplified Network architecture :In multicast tree based routing
the switch structure s pretty complicated , consisting of multicast VC
switches , VP switches and VC switches . On the other hand , in single
connection based scheme the network architecture becomes very simplified
as the maximum no of copies a cell needs to generate is two as compared
to tree based scheme in which thereís no such limit and the no of copies
required at a single switch maybe too large to be supported . Generation
of two copies simplifies the switch architecture greatly. Also only two
types of switches VP and VC( capable of generating 2 copies) are required
. Thus reducing the cost of the network and ATM traffic implementation.
- Virtual Path Retention : Often need arises in wide area networks
with similar traffic over different load periods to retain certain virtual
paths so that they can be retained later. As compared to a multicast tree
it is more prudent to retain the multicast path because in the case of
multicast tree the load is spread out and hence many links may be unnecessarily
wasted, when a whole tree is retained while in the case of a path it is
easier to retain a path and not many links are wasted.
- Integration of CAC and routing algorithm is easily made as CAC
is made a a part of the routing algorithm.


 (
(